Mandelbrot set using assembler
One of the Graphics utilities is a uLisp program to plot the Mandelbrot set.
This page describes how to speed up the program by writing the inner loop in RISC-V machine code using the RISC‑V assembler.
Mandelbrot set in uLisp
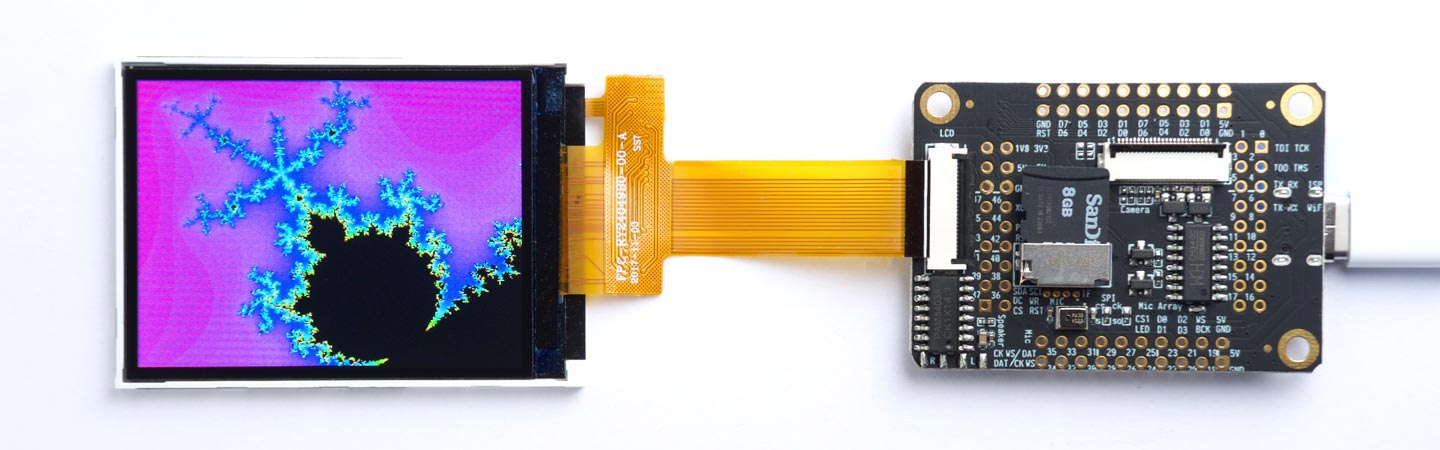
Here's the Mandelbrot set program running on a MAiX One Dock board:
Here's the original program in Lisp, slightly modified to make the inner loop a separate function, iterate:
(defun mandelbrot (x0 y0 scale)
(set-rotation 2)
(fill-screen)
(dotimes (y 240)
(let ((b (+ (/ (- y 120) 120 scale) y0)))
(dotimes (x 320)
(let* ((a (+ (/ (- x 160) 120 scale) x0))
(c (iterate a b)))
(draw-pixel x y (if (plusp c) (hsv (* 359 (/ c 80)) 1 1) 0)))))))
Here's the iterate function:
(defun iterate (a0 b0)
(let ((c 80) (a a0) (b b0) a2)
(loop
(setq a2 (+ (- (* a a) (* b b)) a0))
(setq b (+ (* 2 a b) b0))
(setq a a2)
(decf c)
(when (or (> (+ (* a a) (* b b)) 4) (zerop c)) (return c)))))
These functions also call rgb and hsv to choose the colours for the contours:
(defun rgb (r g b) (logior (ash (logand r #xf8) 8) (ash (logand g #xfc) 3) (ash b -3)))
(defun hsv (h s v)
(let* ((chroma (* v s))
(x (* chroma (- 1 (abs (- (mod (/ h 60) 2) 1)))))
(m (- v chroma))
(i (truncate h 60))
(params (list chroma x 0 0 x chroma))
(r (+ m (nth i params)))
(g (+ m (nth (mod (+ i 4) 6) params)))
(b (+ m (nth (mod (+ i 2) 6) params))))
(rgb (round (* r 255)) (round (* g 255)) (round (* b 255)))))
To plot the whole Mandelbrot set call:
(mandelbrot -0.5 0 1)
The section I displayed in the above photograph is obtained with:
(mandelbrot -0.53 -0.61 11)
For convenience, here's a function go that plots this and returns the time taken:
(defun go () (for-millis () (mandelbrot -0.53 -0.61 11)))
On a MAiX board running at 400 MHz the uLisp version takes 230 seconds.
Converting the iterate function to assembler
To speed up the plotting I rewrote the iterate function in RISC-V assembler, using the assembler written in uLisp.
First load the assembler code from here: RISC-V assembler in uLisp.
Fortunately the K210 processor used on the MAiX boards includes floating-point instructions, so we can use these to perform the arithmetic. I didn't include support for these in the original assembler so they need to be added from here: RISC-V assembler floating-point extensions.
Here's the assembler version of iterate. It's pretty much a direct conversion of the uLisp version above:
(defcode iterate (a b) ($flw 'fa0 8 '(a0)) ;a0 ($flw 'fa1 8 '(a1)) ;b0 ($fmv.s 'ft0 'fa0) ;a ($fmv.s 'ft1 'fa1) ;b ($li 'a4 2) ($fcvt.s.w 'ft5 'a4) ; ft5=2 ($li 'a0 80) again ($fmul.s 'ft2 'ft0 'ft0) ($fmul.s 'ft3 'ft1 'ft1) ($fsub.s 'ft4 'ft2 'ft3) ($fadd.s 'ft4 'ft4 'fa0) ;a2 ($fmul.s 'ft6 'ft0 'ft1) ($fmul.s 'ft7 'ft6 'ft5) ($fadd.s 'ft1 'ft7 'fa1) ;b ($fmv.s 'ft0 'ft4) ;a ($addi 'a0 'a0 -1) ($beqz 'a0 ret) ($fmul.s 'ft6 'ft0 'ft0) ($fmul.s 'ft7 'ft1 'ft1) ($fadd.s 'ft7 'ft6 'ft7) ($fcvt.w.s 'a3 'ft7) ($addi 'a3 'a3 -4) ($blez 'a3 again) ret ($ret))
If you assemble this code it will replace the Lisp version, and you can then run (go) again to see the speed improvement.
The version with a machine-code version of iterate takes 43 seconds, over five times faster.
