Adafruit RP2040 Feather boards
These are Adafruit's Feather-format boards based on the RP2040, a microcontroller chip designed by Raspberry Pi in the UK. It's a dual-core ARM Cortex M0+ running at 200 MHz which provides up to 16 MB of off-chip flash and 264 KB on-chip RAM. It has 30 GPIO pins, 4 of which can be used as analogue inputs, two UARTs, two SPI controllers, two I2C controllers, and 16 PWM channels.
Boards
Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger
Installing uLisp from the Arduino IDE
Install the Raspberry Pi Pico/RP2040 core
- Add the following URL to the Additional Boards Manager URLs list in the Arduino IDE Preferences dialog box:
https://github.com/earlephilhower/arduino-pico/releases/download/global/package_rp2040_index.json
- In the Arduino IDE search for the Raspberry Pi Pico/RP2040 core in Boards Manager and install it.
I tested this with core version 4.5.0 which uses the new certified 200 Mhz clock.
- Select Raspberry Pi RP2040 Boards from the Board menu, and Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger as appropriate from the submenu.
- Set Flash Size to the option that gives FS: 1MB. On the Raspberry Pi Pico this is 8MB (Sketch: 7MB, FS: 1MB).
This allocates enough space for use by LittleFS to save the entire workspace with save-image.
You can leave all the other options at their defaults.
Upload uLisp
- Download the latest ARM version of uLisp from the Download uLisp page.
- Select the board's USB port from the Port menu
- To use the SD card interface on the Adafruit Adalogger board uncomment this line at the start of the uLisp source before uploading uLisp:
#define sdcardsupport
- Upload uLisp to the board.
Using uLisp
- You may need to select the board's USB port from the Port menu again.
- Select Serial Monitor from the Tools menu.
- Enter Lisp commands.
Putting the board into upload mode
If the upload fails you may need to put the board into upload mode first.
- Press and hold the Boot.
- Press the Reset button.
- Release the Boot button.
Error on save-image
If when you call save-image you get the error;
Error: 'save-image' problem saving to LittleFS
the most likely explanation is that you didn't set the Flash Size option to the appropriate value to reserve memory for LittleFS before uploading uLisp.
ARM assembler
The ARM version of uLisp includes an ARM assembler that allows you to generate machine-code functions, integrated with Lisp, written in ARM thumb code. The assembler itself is written in Lisp to make it easy to extend it or add new instructions. For more information see ARM assembler overview.
Programming the RP2040 registers
For details of directly programming the RP2040 registers from uLisp see Programming ARM registers.
Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger [1] is a new RP2040 Feather-format board that includes 8 Mbytes of flash, and a microSD socket, ideal for use with uLisp:
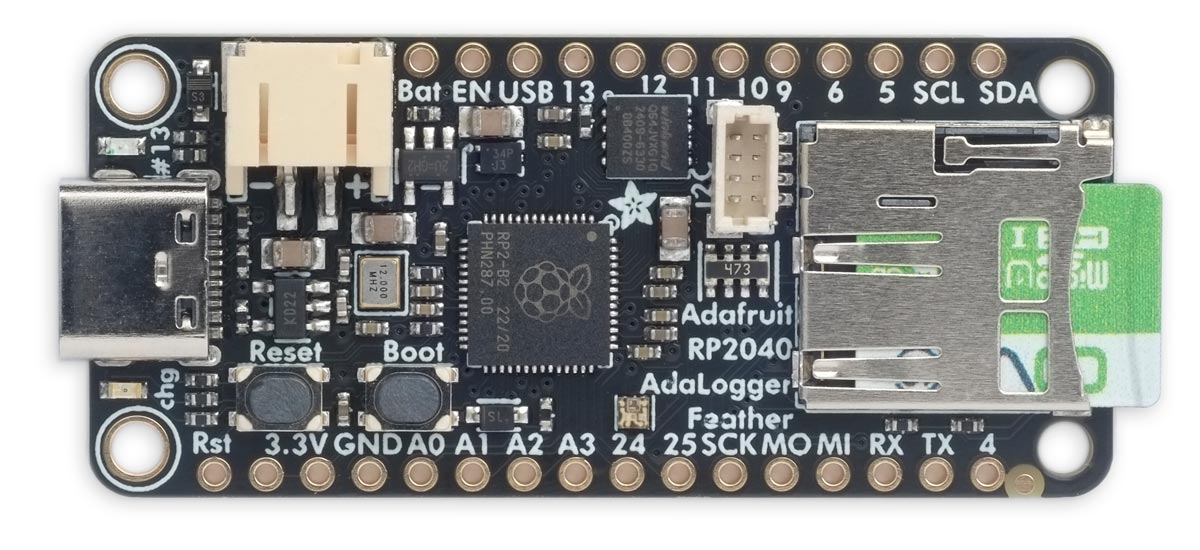
It has the following features:
- A NeoPixel RGB LED.
- A Stemma QT connector giving access to the I2C port.
- LiPo battery connector, with charging via the USB C port.
Pins
For details of the pin connections see Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger.
SD card interface
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger includes a micro SD card socket, which you can use to write to and read from SD cards using uLisp.
You can read a list of the filenames of the files on the SD card with the command:
(directory)
When the SD card interface is selected, Lisp images are also saved to and read from the SD card, and you have the option of saving multiple named Lisp image files.
LED
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger has a red LED connected to :led-builtin (digital pin 13) which you can flash with the following program:
(defun blink (&optional x) (pinmode :led-builtin t) (digitalwrite :led-builtin x)
(delay 1000) (blink (not x)))
Run it by typing:
(blink t)
This pin can also be used as an analogue pin, so you can pulsate the red LED slowly on and off with the program:
(defun pulse ()
(let (down)
(loop
(dotimes (x 256)
(delay 5)
(analogwrite :led-builtin (if down (- 255 x) x)))
(setq down (not down)))))
Run it by typing:
(pulse)
Exit from either program by entering ~.
NeoPixel LED
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger also has a NeoPixel on pin 17. The NeoPixel is driven by the 3.3V supply.
Analogue inputs
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger has 4 analogue inputs, on pins 26 to 29.
Analogue outputs
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger supports PWM on all pins, with some restrictions; for details see the Adafruit documentation [2].
Serial
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger has one serial port, Serial1, on pin numbers 1 (RX) and 0 (TX). By default the baud rate is 9600.
SPI
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger has two SPI ports: SPI0 on pin numbers 8 (MISO), 15 (MOSI), 14 (SCK), and 13 (SS); and SPI1, which is used by the SD card socket, on pin numbers 20 (MISO), 19 (MOSI), and 18 (SCK), and 23 (SS). There is also a card detect signal on pin 16.
I2C
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger has one accessible I2C port, Port 0 on pin numbers 2 (SDA) and 3 (SCL). It is also available on the STEMMA QT connector.
Button
The Boot button can be read on pin 7.
Adafruit Feather RP2040
This is Adafruit's original RP2040-based board in their Feather format [3]. It includes a NeoPixel LED and an 8 MByte DataFlash chip:
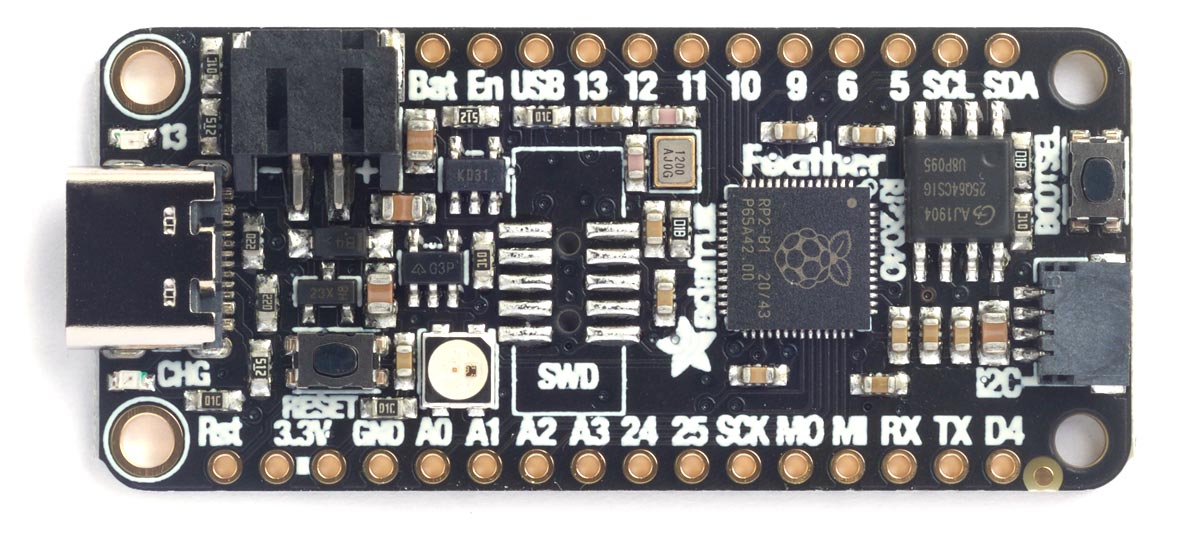
At one point they made a pink version of this board! A Stemma QT connector lets you daisy-chain I2C sensors and displays.
Pins
For details of the pin connections see Adafruit Feather RP2040.
LED
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 has a red LED connected to the digital pin 13 which you can flash with the following program:
(defun blink (&optional x) (pinmode :led-builtin t) (digitalwrite :led-builtin x)
(delay 1000) (blink (not x)))
Run it by typing:
(blink)
All pins can also be used for analogue (PWM) output, so you can pulsate the LED slowly on and off with the program:
(defun pulse ()
(let (down)
(loop
(dotimes (x 256)
(delay 5)
(analogwrite :led-builtin (if down (- 255 x) x)))
(setq down (not down)))))
Run it by typing:
(pulse)
Exit from either program by entering ~.
Analogue inputs
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 has four analogue inputs which you can access on digital pins 26 to 29. They have 12-bit precision.
Analogue outputs
You can generate an analogue output using PWM on any of the digital pins 0 to 29. By default the precision is 8 bits, but you can change it to a value from 4 to 16 bits by calling, for example:
(analogwriteresolution 16)
Playing notes
You can use the note function to play tunes on any pin. For example, the following function scale plays the scale of C on the specified pin:
(defun scale (pin) (mapc (lambda (n) (note pin n 4) (delay 500)) '(0 2 4 5 7 9 11 12)) (note))
For example, connect a piezo speaker between digital pin 10 and GND, and evaluate:
(scale 10)
Serial
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 has one accessible serial port: Serial1 on pin numbers 0 (TX) and 1 (RX).
SPI
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 has one accessible SPI port: SPI0 on pin numbers 20 (MISO), 19 (MOSI), 18 (SCK) and 17 (SS).
I2C
The Adafruit Feather RP2040 has one accessible I2C port: Wire1 on pin numbers 2 (SDA) and 3 (SCL), which also go to the Stemma QT connector.
- ^ Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger on Adafruit.
- ^ Adafruit Feather RP2040 Adalogger Overview on Adafruit.
- ^ Adafruit Feather RP2040 on Adafruit.
